#Microprocessor and GPU Market
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Microprocessor and GPU Market by Architecture, Functionality, GPU Type, Deployment, Application (Consumer Electronics, Server and Data Center, Automotive, BFSI, Industrial), and Geography
0 notes
Text
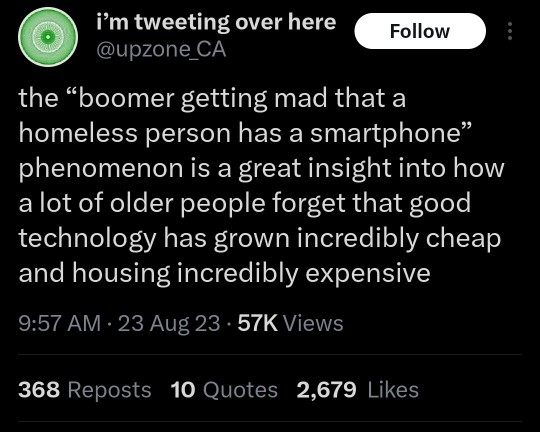
Let’s not forget what several years worth of Pew Research studies taught us:
Computers (or smartphones) are no longer a hobby or luxury, but a virtual necessity to do everything in American society; apply for jobs, do jobs (if working from home), organize childcare, take classes, organize schoolwork, do research, manage banking and finances, send and receive money, sell things, manage medical appointments (often through apps) and prescriptions, on top of communication with your family, your child’s teachers, your caseworker, etc.
The phone company isn’t exactly running fiber internet to people in tents, are they?
In areas with poor broadband access, your phone is the internet for many people. This contributes to the “digital divide” and why, IMHO, the USPS should get into the broadband business and serve those underserved areas with subsidized connections.
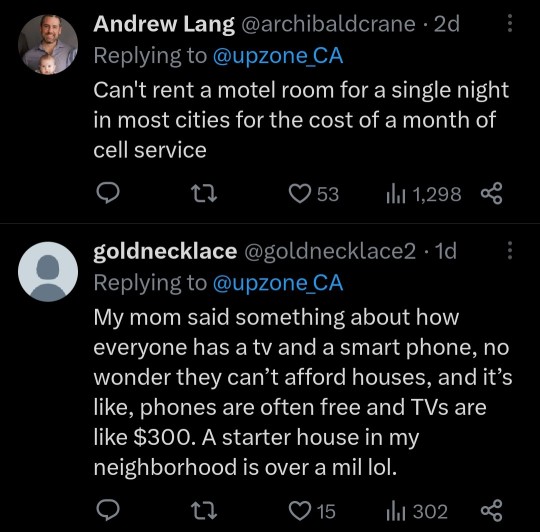
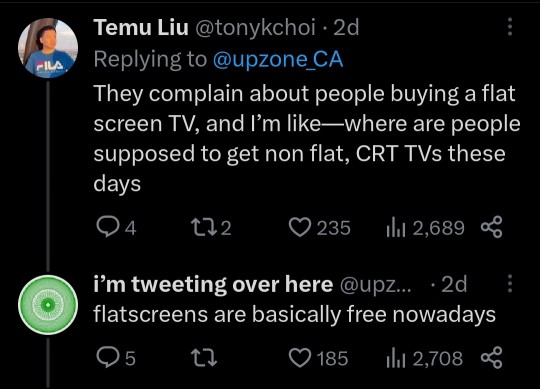
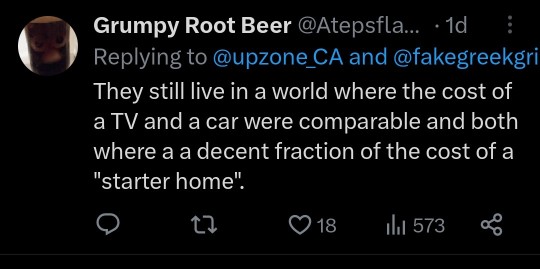
I was shocked how cheap TVs had become. I got a 4K OLED for less than my old 1080p LCD cost. A basic 24” Insignia 720p TV can be had, as of September 2023, for $79.
What this illustrates is the difference between commodities and positional goods. As we saw during the pandemic, supply lines for manufactured items were constrained, causing prices to temporarily rise, but overall, the price of consumer electronics have fallen sharply year-over-year, or have gotten much more powerful for the same price. The internal design of many products has become simplified, with functions that used to require multiple discrete microprocessors now absorbed into so-called “systems on a chip” or SoCs.

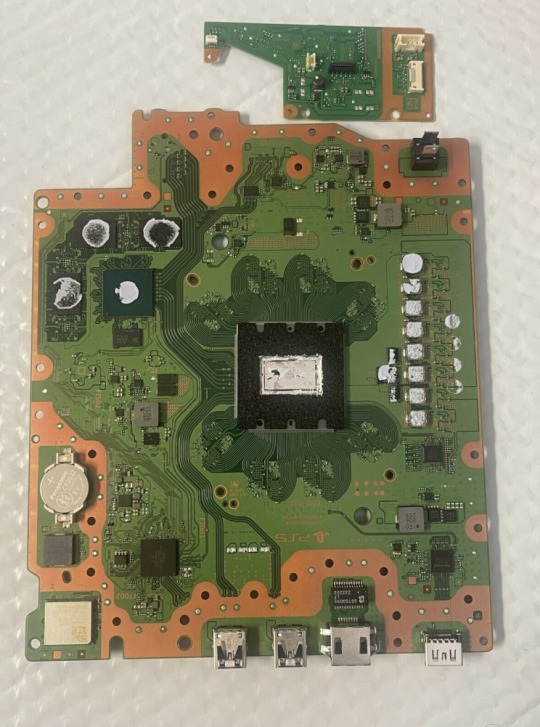
Left: PlayStation 1 motherboard, 1994. Separate custom microprocessors are visible, including the CPU, GPU, audio processor, system memory and hardware interface chips.
Right: PlayStation 5 motherboard, 2020. The CPU and GPU are merged onto a single custom SoC made by AMD; the rest is just a couple of motherboard chips and a set of power transistors. Roughly, it’s 5,000 times more powerful than its ancestor.
If that were true for housing, we’d all be living in automated mansions that cost $100.
However, housing is a positional good.
While I occupy a house in a desirable, walkable neighborhood with access to transit, somebody else cannot. I have to vacate this unit for someone else to get it. People cannot just buy their way into this neighborhood if nobody’s selling.
Due to geography, zoning, infrastructure limits and other factors, the number of such desirable units is limited and thus they become more expensive to buy or rent.
Add all the other factors - Airbnbs, private equity, and flippers taking units off the market, nimby resistance to new denser housing, and disinvestment in public housing, and you have a perfect storm of unaffordability.
The only solution, really, is to institute strong market controls to end speculation, end institutional Airbnb hoarding, put in rent controls, and build way more public and cooperative housing that’s off the market.
42K notes
·
View notes
Text
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Text
Chiplets and AI: A Match Made for the Future of Computing

The Chiplets Market is set to redefine semiconductor technology, with an estimated CAGR of 46.47% between 2024 and 2034. The market, valued at $7.1 billion in 2023, is projected to soar to $555 billion by 2034, driven by high-performance computing (HPC), artificial intelligence (AI), and advancements in packaging technologies.
The shift from monolithic chip designs to modular chiplet architectures is accelerating as industries demand more efficient, scalable, and high-performing semiconductor solutions.
What Are Chiplets?
Chiplets are small, modular semiconductor components that combine different processing elements—CPUs, GPUs, AI accelerators, and memory units—within a single package. Unlike traditional monolithic chips, chiplets provide greater flexibility, faster development cycles, and improved performance optimization for specific applications.
This modular approach is crucial for industries requiring high-speed processing, such as AI, data centers, and autonomous vehicles.
Key Market Drivers
1. Rising Demand for High-Performance Computing (HPC)
Industries such as AI, machine learning, and deep learning require powerful computing solutions to process vast amounts of data efficiently. Chiplet architectures enable customized processor configurations, optimizing performance for specific workloads.
2. Breakthroughs in Advanced Packaging Technologies
Innovative 2.5D and 3D packaging solutions allow better integration, reduced latency, and enhanced energy efficiency. Semiconductor leaders like Intel, AMD, and TSMC are investing heavily in heterogeneous integration and advanced interconnect technologies to maximize chiplet efficiency.
3. Geopolitical Influence on Semiconductor Manufacturing
The U.S., China, and Europe are actively investing in domestic semiconductor production to reduce dependency on foreign supply chains. The U.S. CHIPS Act and similar government initiatives are driving funding into chiplet research, production facilities, and infrastructure.
Microprocessors (MPUs) Dominating the Chiplets Market
The MPUs segment held a 49.8% market share in 2023 and is expected to expand at a 44.19% CAGR by 2034. With chiplets, MPU manufacturers can customize architectures for AI-driven applications, edge computing, and autonomous systems.
Regional Outlook: Asia-Pacific Leads the Market
Asia-Pacific captured 38.6% of the chiplets market in 2023 and is projected to grow at a 47.6% CAGR through 2034. Countries like Taiwan, South Korea, and China dominate chiplet production due to their established semiconductor ecosystems and manufacturing capabilities.
Key Players Shaping the Chiplets Market
The global chiplets market is consolidated, with major players including:
Advanced Micro Devices (AMD)
Intel Corporation
Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC)
Marvell Technology
Nvidia Corporation
Samsung Electronics
Apple Inc.
These companies are investing in R&D, strategic partnerships, and mergers & acquisitions to expand their chiplet product portfolios.
Future Trends in the Chiplets Market
✅ Expansion of AI and Machine Learning Applications Chiplets will play a vital role in developing AI-powered computing systems that demand faster, more efficient data processing.
✅ Adoption of Advanced Chiplet Packaging Innovations in 3D stacking, silicon interposers, and hybrid bonding will enhance chiplet performance and energy efficiency.
✅ Growing Investment in Semiconductor Manufacturing With government subsidies and private investments, companies are rapidly expanding chiplet production capacity worldwide.
Conclusion
The chiplets market is on an exponential growth trajectory, driven by HPC demand, technological advancements, and geopolitical shifts. As the industry transitions from monolithic chips to modular architectures, chiplets will be the foundation for next-generation AI, data centers, and IoT applications.
Semiconductor giants are racing to dominate the chiplet market, making 2034 an era of rapid chip innovation.
Contact Us: Transparency Market Research Inc. CORPORATE HEADQUARTER DOWNTOWN, 1000 N. West Street, Suite 1200, Wilmington, Delaware 19801 USA Tel: +1-518-618-1030 USA - Canada Toll Free: 866-552-3453 Website: https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com Email: [email protected]
0 notes
Text
Intel vs AMD: A Deep Dive into the Ongoing Processor Battle
In the ever-evolving world of computer hardware, Intel and AMD have been locked in a fierce competition for processor supremacy. This rivalry has fueled tremendous innovation, pushing both companies to create CPUs that offer the best performance, efficiency, and value for consumers. From their historical beginnings to the current market dynamics, this battle continues to shape the landscape of modern computing.
Historical Background
The Intel vs. AMD rivalry dates back to the 1980s when AMD entered the microprocessor market. Intel had already established itself as the dominant player with its x86 architecture, but AMD quickly became a worthy adversary by introducing processors that were compatible with Intel’s design while also offering more affordable alternatives. This competition laid the foundation for a series of innovations, where both companies continually sought to outpace each other in speed, efficiency, and features.
Over the years, Intel and AMD have each pushed the boundaries of CPU technology. Their rivalry has given consumers a wide variety of processors to choose from, catering to diverse needs and budgets, thus benefiting the tech community at large.
Current Market Dynamics
Today, Intel and AMD continue to battle for market share across multiple segments, including consumer desktops and laptops, high-performance computing, and server markets. Both companies offer a range of processors designed for specific use cases, leading to competitive pricing and performance improvements.
Consumer Desktops and Laptops
In the consumer market, Intel and AMD target users with different performance levels. Intel’s Core i3, i5, i7, and i9 series compete directly with AMD’s Ryzen 3, 5, 7, and 9 processors. The choice often boils down to individual needs—whether it's gaming, content creation, or multitasking.
AMD has made notable strides in recent years with its Ryzen series, which provides more cores and threads than Intel’s offerings at similar price points. This makes AMD appealing to users requiring excellent multi-threaded performance for tasks like video editing, rendering, and gaming.
High-Performance Computing
For power users in fields like 3D modeling, video production, and scientific simulations, Intel’s Core X-Series and AMD’s Ryzen Threadripper are the go-to processors. Both companies have focused on delivering top-tier performance for these demanding applications, often leveraging cutting-edge technology to gain an edge.
Server and Data Center
The battle extends to the server and data center markets, where Intel’s Xeon processors and AMD’s EPYC chips compete for dominance. AMD has made significant inroads with EPYC, challenging Intel’s long-standing lead in this space with processors that offer high core counts and superior performance-per-dollar ratios.
Key Differentiators
Several factors differentiate Intel and AMD processors, influencing the choice of consumers and businesses alike.
Architecture: Intel uses its x86 architecture, while AMD employs its AMD64 architecture. Both designs differ in instruction execution and power efficiency.
Manufacturing Process: Both companies have advanced their manufacturing processes. Intel historically led in this area, but AMD has caught up with its shift to 7nm and 5nm processes, closing the performance gap.
Integrated Graphics: Intel processors often feature integrated graphics. At the same time, AMD’s Ryzen chips also offer integrated Radeon graphics, making them strong contenders for users who want decent graphics performance without a dedicated GPU.
Price-Performance Ratio: AMD has built a reputation for offering competitive price-to-performance ratios, providing more cores at lower prices. Intel, however, focuses on specialized features like Quick Sync for video encoding and Thunderbolt support.
Conclusion
The Intel vs. AMD rivalry continues to drive advancements in CPU technology, ensuring consumers have access to cutting-edge, competitively priced processors. Whether you're focused on gaming, content creation, or enterprise-level computing, both companies offer compelling options that cater to various needs. Ultimately, the ongoing competition between Intel and AMD benefits consumers, guaranteeing powerful, efficient processors and pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in computing.
Want to Buy Intel and AMD CPUs in Bulk at Affordable Prices from VSTL?
VSTL offers a wide selection of processors from leading brands, ensuring high performance, efficiency, and competitive pricing. Whether you need processors for desktops, laptops, or high-performance computing, VSTL provides bulk purchasing options tailored to your needs. With access to the latest models and excellent customer service, buying Intel and AMD CPUs in bulk from VSTL is a smart choice for businesses and tech enthusiasts looking to save while upgrading their systems.
0 notes
Text
The Rise of AMD: A Look at their Advancements in CPU Technology
In recent years, AMD has been making waves in the tech industry with their innovative advancements in CPU technology. From challenging competitors to pushing the boundaries of performance, AMD has solidified its position as a major player in the market. In this article, we will explore the key advancements Find out more that have propelled AMD to the forefront of the industry and examine how they are shaping the future of computing.
Introduction
AMD, short for Advanced Micro Devices, is a semiconductor company known for its cutting-edge CPUs and GPUs. Founded in 1969, AMD has a long history of innovation and has established itself as a formidable competitor to industry giants like Intel and Nvidia. With a focus on pushing the boundaries of performance and efficiency, AMD has consistently delivered products that cater to both consumers and professionals alike.
The Evolution of AMD Processors The Early Days: A Brief History of AMD
AMD vs Competition: In the early days, AMD primarily focused on manufacturing second-source microprocessors for companies like Intel. However, it wasn't until the launch of the AMD K5 processor in 1996 that they began to establish themselves as a serious contender in the market. The K5 marked the beginning of AMD's journey towards developing their own line of processors that could rival Intel's offerings.
The Athlon Era
AMD at GPU: In 1999, AMD introduced the Athlon processor, which quickly gained popularity for its impressive performance and competitive pricing. The success of the Athlon series laid the foundation for future innovations from AMD and firmly established them as a major player in the CPU market. Around this time, AMD also made significant strides in GPU technology with their Radeon graphics cards, further solidifying their position as a leading tech company.
Ryzen Revolution
Innovative Technologies of AMD: Fast forward to 2017, when AMD launched their Ryzen line of processors based on their Zen architecture. The Ryzen CPUs marked a significant leap forward in terms of performance and efficiency, offering consumers a viable alternative to Intel's offerings. With features like simultaneous multithreading (SMT) and Precision Boost technology, Ryzen processors quickly gained a reputation for being powerful yet affordable options for gamers and content creators alike.

Advancements in CPU Technology Zen 2 Architecture
The Rise of AMD: A Look at Their Advancements in CPU Technology: One of the most significant advancements from AMD in recent years has been the introduction of their Zen 2 architecture. Built on a 7nm process node, Zen 2 CPUs offer improved IPC (instructions per cycle) performance and higher clock speeds compared to previous generations. This architectural leap has allowed AMD to compete head-to-head with Intel's offerings across various market segments.
youtube
Chiplet Design
AMD and AI: Another key innovation from AMD is their chiplet design approach, which involves using multiple smaller dies interconnected on a single package. This modular design allows for greater scalability and efficiency compared to traditional monolithic designs. By leveraging chiplets, AMD can optimize performance while reducing costs associated with manufacturing larger monolithic dies.
Infinity Fabric Interconnect
One of the key technologies that enable AMD's chiplet design is their Infinity Fabric int
1 note
·
View note
Text
Semiconductorinsight reports
Wide Bandgap Semiconductor Market - https://semiconductorinsight.com/report/wide-bandgap-semiconductor-market/
Wireless Charging Market - https://semiconductorinsight.com/report/wireless-charging-market/
3D IC Market - https://semiconductorinsight.com/report/3d-ic-market/
Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) Market - https://semiconductorinsight.com/report/analog-to-digital-converter-adc-market/
Application Processor Market - https://semiconductorinsight.com/report/application-processor-market/
Audio IC Market - https://semiconductorinsight.com/report/audio-ic-market/
Bluetooth IC Market - https://semiconductorinsight.com/report/bluetooth-ic-market/
CMOS Image Sensor Market - https://semiconductorinsight.com/report/cmos-image-sensor-market/
Data Converter Market - https://semiconductorinsight.com/report/data-converter-market/
Digital Signal Processor (DSP) Market - https://semiconductorinsight.com/report/digital-signal-processor-dsp-market/
Display Driver IC Market - https://semiconductorinsight.com/report/display-driver-ic-market/
Embedded Non-Volatile Memory (eNVM) Market - https://semiconductorinsight.com/report/embedded-non-volatile-memory-envm-market/
Field-Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) Market - https://semiconductorinsight.com/report/field-programmable-gate-array-fpga-market/
Flash Memory Market - https://semiconductorinsight.com/report/flash-memory-market/
Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) Market - https://semiconductorinsight.com/report/graphics-processing-unit-gpu-market/
High-Brightness LED Market - https://semiconductorinsight.com/report/high-brightness-led-market/
Image Sensor Market - https://semiconductorinsight.com/report/image-sensor-market/
Integrated Passive Devices (IPD) Market - https://semiconductorinsight.com/report/integrated-passive-devices-ipd-market/
Laser Diode Market - https://semiconductorinsight.com/report/laser-diode-market/
Light Sensor Market - https://semiconductorinsight.com/report/light-sensor-market/
Magnetoresistive RAM (MRAM) Market - https://semiconductorinsight.com/report/magnetoresistive-ram-mram-market/
Micro LED Market - https://semiconductorinsight.com/report/micro-led-market/
Microprocessor Market - https://semiconductorinsight.com/report/microprocessor-market/
Mixed Signal System-on-Chip (SoC) Market - https://semiconductorinsight.com/report/mixed-signal-system-on-chip-soc-market/
NAND Flash Market - https://semiconductorinsight.com/report/nand-flash-market/
Non-Volatile Memory (NVM) Market - https://semiconductorinsight.com/report/non-volatile-memory-nvm-market/
Organic Light Emitting Diode (OLED) Market - https://semiconductorinsight.com/report/organic-light-emitting-diode-oled-market/
Photonic Integrated Circuit (PIC) Market - https://semiconductorinsight.com/report/photonic-integrated-circuit-pic-market/
Power Management IC (PMIC) Market - https://semiconductorinsight.com/report/power-management-ic-pmic-market/
Printed Electronics Market - https://semiconductorinsight.com/report/printed-electronics-market/
Radio Frequency (RF) Front-End Module Market - https://semiconductorinsight.com/report/radio-frequency-rf-front-end-module-market/
Semiconductor Assembly and Testing Services (SATS) Market - https://semiconductorinsight.com/report/semiconductor-assembly-and-testing-services-sats-market/
Semiconductor Laser Market - https://semiconductorinsight.com/report/semiconductor-laser-market/
Silicon Carbide (SiC) Market - https://semiconductorinsight.com/report/silicon-carbide-sic-market/
Smart Card IC Market - https://semiconductorinsight.com/report/smart-card-ic-market/
Smart Sensor Market - https://semiconductorinsight.com/report/smart-sensor-market/
System-in-Package (SiP) Market - https://semiconductorinsight.com/report/system-in-package-sip-market/
Thin Film Transistor (TFT) Market - https://semiconductorinsight.com/report/thin-film-transistor-tft-market/
Touch Controller IC Market - https://semiconductorinsight.com/report/touch-controller-ic-market/
Ultraviolet (UV) LED Market - https://semiconductorinsight.com/report/ultraviolet-uv-led-market/
0 notes
Text
The Rise of AMD: A Look at their Advancements in CPU Technology
In recent years, AMD has been making waves in the tech industry with their innovative advancements in CPU technology. From challenging competitors to pushing the boundaries of performance, AMD has solidified its position as a major player in the market. In this article, we will explore the key advancements that have propelled AMD to the forefront of the industry and examine how they are shaping the future of computing.
Introduction
AMD, short for Advanced Micro Devices, is a semiconductor company known for its cutting-edge CPUs and GPUs. Founded in 1969, AMD has a long history of innovation and has established itself as a formidable competitor to industry giants like Intel and Nvidia. With a focus on pushing the boundaries of performance and efficiency, AMD has consistently delivered products that cater to both consumers and professionals alike.
The Evolution of AMD Processors The Early Days: A Brief History of AMD
AMD vs Competition: In the early days, AMD primarily focused on manufacturing second-source microprocessors for companies like Intel. However, it wasn't until the launch of the AMD K5 processor in 1996 that they began to establish themselves as a serious contender in the market. The K5 marked the beginning of AMD's journey towards developing their own line of processors that could rival Intel's offerings.
The Athlon Era
AMD at GPU: In 1999, AMD introduced the Athlon processor, which quickly gained popularity for its impressive performance and competitive pricing. The success of the Athlon series laid the foundation for future innovations from AMD and firmly established them as a major player in the CPU market. Around this time, AMD also Additional info made significant strides in GPU technology with their Radeon graphics cards, further solidifying their position as a leading tech company.
youtube

Ryzen Revolution
Innovative Technologies of AMD: Fast forward to 2017, when AMD launched their Ryzen line of processors based on their Zen architecture. The Ryzen CPUs marked a significant leap forward in terms of performance and efficiency, offering consumers a viable alternative to Intel's offerings. With features like simultaneous multithreading (SMT) and Precision Boost technology, Ryzen processors quickly gained a reputation for being powerful yet affordable options for gamers and content creators alike.
Advancements in CPU Technology Zen 2 Architecture
The Rise of AMD: A Look at Their Advancements in CPU Technology: One of the most significant advancements from AMD in recent years has been the introduction of their Zen 2 architecture. Built on a 7nm process node, Zen 2 CPUs offer improved IPC (instructions per cycle) performance and higher clock speeds compared to previous generations. This architectural leap has allowed AMD to compete head-to-head with Intel's offerings across various market segments.

Chiplet Design
AMD and AI: Another key innovation from AMD is their chiplet design approach, which involves using multiple smaller dies interconnected on a single package. This modular design allows for greater scalability and efficiency compared to traditional monolithic designs. By leveraging chiplets, AMD can optimize performance while reducing costs associated with manufacturing larger monolithic dies.
Infinity Fabric Interconnect
One of the key technologies that enable AMD's chiplet design is their Infinity Fabric int
1 note
·
View note
Text
The Rise of AMD: A Look at their Advancements in CPU Technology
In recent years, AMD has been making waves in the tech industry with their innovative advancements in CPU technology. From challenging competitors to pushing the boundaries of performance, AMD has solidified its position as a major player in the market. In this article, we will explore the key advancements that have propelled AMD to the forefront of the industry and examine how they are shaping the future of computing.
Introduction
AMD, short for Advanced Micro Devices, is a semiconductor company known for its cutting-edge CPUs and GPUs. Founded in 1969, AMD has a long history of innovation and has established itself as a formidable competitor to industry giants like Intel and Nvidia. With a focus on pushing the boundaries of performance and efficiency, AMD has consistently delivered products that cater to both consumers and professionals alike.
The Evolution of AMD Processors The Early Days: A Brief History of AMD
AMD vs Competition: In the early days, AMD primarily focused on manufacturing second-source microprocessors for companies like Intel. However, it wasn't until the launch of the AMD K5 processor in 1996 that they began to establish themselves as a serious contender in the market. The K5 marked the beginning of AMD's journey towards developing their own line of processors that could rival Intel's offerings.

youtube
The Athlon Era
AMD at GPU: In 1999, AMD introduced the Athlon processor, which quickly gained popularity for its impressive performance and competitive pricing. The success of the Athlon series laid the foundation for future innovations from AMD and firmly established them as a major player in the CPU market. Around this time, AMD also made significant strides in GPU technology with their Radeon graphics cards, further solidifying their position as a leading tech company.
Ryzen Revolution
Innovative Technologies of AMD: Fast forward to 2017, when AMD launched their Ryzen line of processors based on their Zen architecture. The Ryzen CPUs marked a significant leap forward in terms of performance and efficiency, offering consumers a viable alternative to Intel's offerings. With features like simultaneous multithreading (SMT) and Precision Boost technology, Ryzen processors quickly gained a reputation for being powerful yet affordable options for gamers and content creators alike.
Advancements in CPU Technology Zen 2 Architecture
The Rise of AMD: A Look at Their Advancements in CPU Technology: One of the most significant advancements from AMD in recent years has been the introduction of their Zen 2 architecture. Built on a 7nm process node, Zen 2 CPUs offer improved IPC (instructions per cycle) performance and higher clock speeds compared to previous generations. This architectural leap has allowed AMD to compete head-to-head with Intel's offerings across various market segments.

Chiplet Design
AMD and AI: Another key innovation from AMD is their chiplet design approach, which involves using multiple smaller dies interconnected on a single package. This modular design allows for greater scalability and efficiency compared to traditional monolithic designs. By leveraging chiplets, AMD can optimize performance while reducing costs associated Additional reading with manufacturing larger monolithic dies.
Infinity Fabric Interconnect
One of the key technologies that enable AMD's chiplet design is their Infinity Fabric int
1 note
·
View note
Text
Semiconductor Chips Explained: Different Types and Their Uses

In today’s fast-paced technological landscape, there is a growing demand for faster and more efficient devices. This need, however, brings a significant challenge: balancing cost and energy consumption while enhancing the performance and functionality of electronic gadgets.
Introduction to Semiconductor Chips
Semiconductor chips are crucial in this regard. The global semiconductor market is projected to reach $687 billion by 2025, showcasing the transformative impact of these chips across various sectors, from computers and smartphones to advanced AI systems and IoT devices. Let's delve deeper into this billion-dollar industry.
What Is A Semiconductor Chip?
A semiconductor chip, also known as an integrated circuit or computer chip, is a small electronic device made from semiconductor materials like silicon. It contains millions or even billions of transistors, which are tiny electronic components capable of processing and storing data.
These chips are the backbone of modern technology, found in a vast array of electronic devices including computers, smartphones, cars, and medical equipment. Manufacturing semiconductor chips involves a complex, multi-step process that includes slicing silicon wafers, printing intricate circuit designs, and adding multiple layers of components and interconnects. Leading companies in the semiconductor industry include Samsung, TSMC, Qualcomm, Marvell, and Intel.
Types of Semiconductor Chips
Memory Chips
Function: Store data and programs in computers and other devices.
Types:
RAM (Random-Access Memory): Provides temporary workspaces.
Flash Memory: Stores information permanently.
ROM (Read-Only Memory) and PROM (Programmable Read-Only Memory): Non-volatile memory.
EPROM (Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory) and EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory): Can be reprogrammed.
Microprocessors
Function: Contain CPUs that power servers, PCs, tablets, and smartphones.
Architectures:
32-bit and 64-bit: Used in PCs and servers.
ARM: Common in mobile devices.
Microcontrollers (8-bit, 16-bit, and 24-bit): Found in toys and vehicles.
Graphics Processing Units (GPUs)
Function: Render graphics for electronic displays, enhancing computer performance by offloading graphics tasks from the CPU.
Applications: Modern video games, cryptocurrency mining.
Commodity Integrated Circuits (CICs)
Function: Perform repetitive tasks in devices like barcode scanners.
Types:
ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits): Custom-designed for specific tasks.
FPGAs (Field-Programmable Gate Arrays): Customizable after manufacturing.
SoCs (Systems on a Chip): Integrate all components into a single chip, used in smartphones.
Analog Chips
Function: Handle continuously varying signals, used in power supplies and sensors.
Components: Include transistors, inductors, capacitors, and resistors.
Mixed-Circuit Semiconductors
Function: Combine digital and analog technologies, used in devices requiring both types of signals.
Examples: Microcontrollers with ADCs (Analog-to-Digital Converters) and DACs (Digital-to-Analog Converters).
Manufacturing Process of Semiconductor Chips
Semiconductor device fabrication involves several steps to create electronic circuits on a silicon wafer. Here’s an overview:
Wafer Preparation: Silicon ingots are shaped and sliced into thin wafers.
Cleaning and Oxidation: Wafers are cleaned and oxidized to form a silicon dioxide layer.
Photolithography: Circuit patterns are transferred onto wafers using UV light and photoresist.
Etching: Unwanted material is removed based on the photoresist pattern.
Doping: Ions are implanted to alter electrical properties.
Deposition: Thin films of materials are deposited using CVD or PVD techniques.
Annealing: Wafers are heated to activate dopants and repair damage.
Testing and Packaging: Finished wafers are tested, diced into individual chips, and packaged for protection.
Conclusion
Semiconductor chips are fundamental to the functionality of nearly every electronic device we use today. They have revolutionized technology by enabling faster, smaller, and more powerful devices. While the semiconductor industry has fueled job creation and economic growth, it also faces challenges related to sustainability and environmental impact. As we continue to push the boundaries of innovation, ethical practices are essential to ensure semiconductors remain vital to our modern world and shape our future.
0 notes
Text
Microprocessor and GPU Market with COVID-19 Impact Analysis by Architecture, Functionality, GPU Type, Deployment, Application (Consumer Electronics, Server and Data Center, Automotive, BFSI, Industrial), and Geography
0 notes
Text
The Rise of AMD: A Look at their Advancements in CPU Technology
In recent years, AMD has been making waves in the tech industry with their innovative advancements in CPU technology. From challenging competitors to pushing the boundaries of performance, AMD has solidified its position as a major player in the market. In this article, we will explore the key advancements that have propelled AMD to the forefront of the industry and examine how they are shaping the future of computing.
Introduction
AMD, short for Advanced Micro Devices, is a semiconductor company known for its cutting-edge CPUs and GPUs. Founded in 1969, AMD has a long history of innovation and has established itself as a formidable competitor to industry Article source giants like Intel and Nvidia. With a focus on pushing the boundaries of performance and efficiency, AMD has consistently delivered products that cater to both consumers and professionals alike.
The Evolution of AMD Processors The Early Days: A Brief History of AMD
AMD vs Competition: In the early days, AMD primarily focused on manufacturing second-source microprocessors for companies like Intel. However, it wasn't until the launch of the AMD K5 processor in 1996 that they began to establish themselves as a serious contender in the market. The K5 marked the beginning of AMD's journey towards developing their own line of processors that could rival Intel's offerings.
The Athlon Era
AMD at GPU: In 1999, AMD introduced the Athlon processor, which quickly gained popularity for its impressive performance and competitive pricing. The success of the Athlon series laid the foundation for future innovations from AMD and firmly established them as a major player in the CPU market. Around this time, AMD also made significant strides in GPU technology with their Radeon graphics cards, further solidifying their position as a leading tech company.
Ryzen Revolution
Innovative Technologies of AMD: Fast forward to 2017, when AMD launched their Ryzen line of processors based on their Zen architecture. The Ryzen CPUs marked a significant leap forward in terms of performance and efficiency, offering consumers a viable alternative to Intel's offerings. With features like simultaneous multithreading (SMT) and Precision Boost technology, Ryzen processors quickly gained a reputation for being powerful yet affordable options for gamers and content creators alike.

Advancements in CPU Technology Zen 2 Architecture
The Rise of AMD: A Look at Their Advancements in CPU Technology: One of the most significant advancements from AMD in recent years has been the introduction of their Zen 2 architecture. Built on a 7nm process node, Zen 2 CPUs offer improved IPC (instructions per cycle) performance and higher clock speeds compared to previous generations. This architectural leap has allowed AMD to compete head-to-head with Intel's offerings across various market segments.
youtube
Chiplet Design
AMD and AI: Another key innovation from AMD is their chiplet design approach, which involves using multiple smaller dies interconnected on a single package. This modular design allows for greater scalability and efficiency compared to traditional monolithic designs. By leveraging chiplets, AMD can optimize performance while reducing costs associated with manufacturing larger monolithic dies.
Infinity Fabric Interconnect
One of the key technologies that enable AMD's chiplet design is their Infinity Fabric int
1 note
·
View note
Text
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Text
The Rise of AMD: A Look at their Advancements in CPU Technology
In recent years, AMD has been making waves in the tech industry with their innovative advancements in CPU technology. From challenging competitors to pushing the boundaries of performance, AMD has solidified its position as a major player in the market. In this article, we will explore the key advancements that have propelled AMD to the forefront of the industry and examine how they are shaping the future of computing.
Introduction
AMD, short for Advanced Micro Devices, is a semiconductor company known for its cutting-edge CPUs and GPUs. Founded in 1969, AMD has a long history of innovation and has established itself as a formidable competitor to industry giants like Intel and Nvidia. With a focus on pushing the boundaries of performance and efficiency, AMD has consistently delivered products that cater to both consumers and professionals alike.
The Evolution of AMD Processors The Early Days: A Brief History of AMD
AMD vs Competition: In the early days, AMD primarily focused on manufacturing second-source microprocessors for companies like Intel. However, it wasn't until the launch of the AMD K5 processor in 1996 that they began to establish themselves as a serious contender in the market. The K5 marked the beginning of AMD's journey towards developing their own line of processors that could rival Intel's offerings.
The Athlon Era
AMD at GPU: In 1999, AMD introduced the Athlon processor, which quickly gained popularity for its impressive performance and competitive pricing. The success of the Athlon series laid the foundation for future innovations from AMD and firmly established them as a major player in the CPU market. Around this time, AMD also made significant strides in GPU technology with their Radeon graphics cards, further solidifying their position as a leading tech company.
Ryzen Revolution
Innovative Technologies of AMD: Fast forward to 2017, when AMD launched their Ryzen line of processors based on their Zen architecture. The Ryzen CPUs marked a significant leap forward in terms of performance and efficiency, offering consumers a viable alternative to Intel's offerings. With features like simultaneous multithreading (SMT) and Precision Boost technology, Ryzen processors quickly gained a reputation for being powerful yet affordable options for gamers and content creators alike.
Advancements in CPU Technology Zen 2 Architecture
The Rise of AMD: A Look at Their Advancements in CPU Technology: One of the most significant advancements from AMD in recent years has been the introduction of their Zen 2 architecture. Built on a 7nm process node, Zen 2 CPUs offer improved IPC (instructions per cycle) performance and higher clock speeds compared to previous generations. This architectural leap has allowed AMD to compete head-to-head with Intel's offerings across various market segments.
youtube
Chiplet Design
AMD and AI: Another key innovation from AMD is their chiplet design approach, which involves using multiple smaller dies interconnected on a single package. This modular design allows for greater scalability and efficiency compared to traditional monolithic designs. By leveraging chiplets, AMD can optimize performance while reducing costs associated with manufacturing larger monolithic dies.

Infinity Fabric Interconnect
One of the key technologies that enable AMD's chiplet design is their Browse this site Infinity Fabric int
1 note
·
View note